Preventive Care Through AI
Nanox.AI solutions analyze routine medical CT scans for any clinical indication to help identify patients with asymptomatic or undetected findings correlated with chronic conditions in cardiac, liver and bone, promoting preventive care management.
Up to 33% of adults and 75% of older adults in the world suffer from multiple chronic conditions, which are often undiagnosed, increasing chances of hospitalization and death. This was a devastating reality during the COVID-19 pandemic, as over 7 million people worldwide died from a combination of the virus and complications from poorly managed chronic disease(s).
Broad Suite of FDA 510(k) Cleared Solutions
AI Cardiac Solution
AI Cardiac Solution
HealthCCSng
FDA 510k CLEARED | CE MARKED
KEY HEALTH CONDITION
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
AI Bone Solution
AI Bone Solution
HealthOST
FDA CLEARED | CE MARKED
& measures bone mineral density in chest and abdominal CT scans.
KEY HEALTH CONDITION
Osteoporosis
AI Liver Solution
AI Liver Solution
HealthFLD
FDA 510k CLEARED
KEY HEALTH CONDITION
Fatty Liver disease: Hepatic steatosis-MASLD (NAFLD),
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)
Empowering Data to Make an Impact
Proven Value
By using Nanox.AI’s cardiac solution, Corewell Health significantly increased their ability to detect coronary calcification, identifying nearly 4,000 new patients in 2023 compared to just 268 patients having CAC reported in the previous two years.

Frederick Meijer Heart and Vascular Institute
Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids, MI Clinical
Professor, MSU School of Medicine
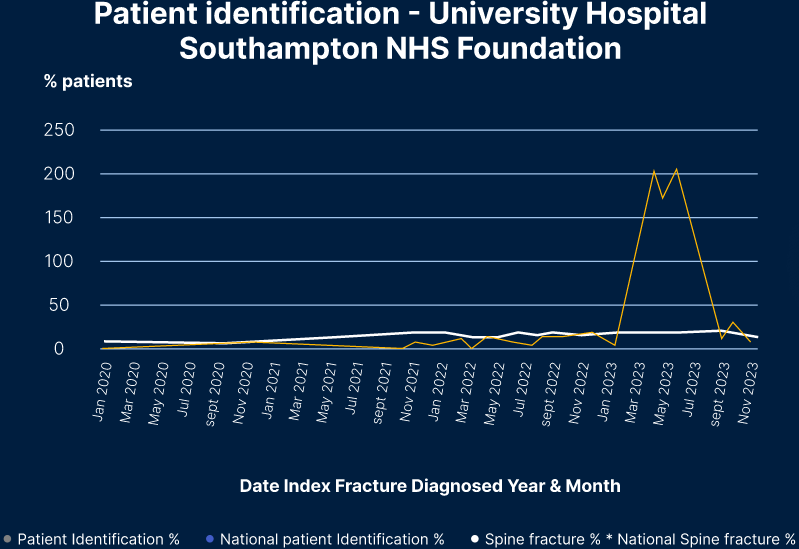
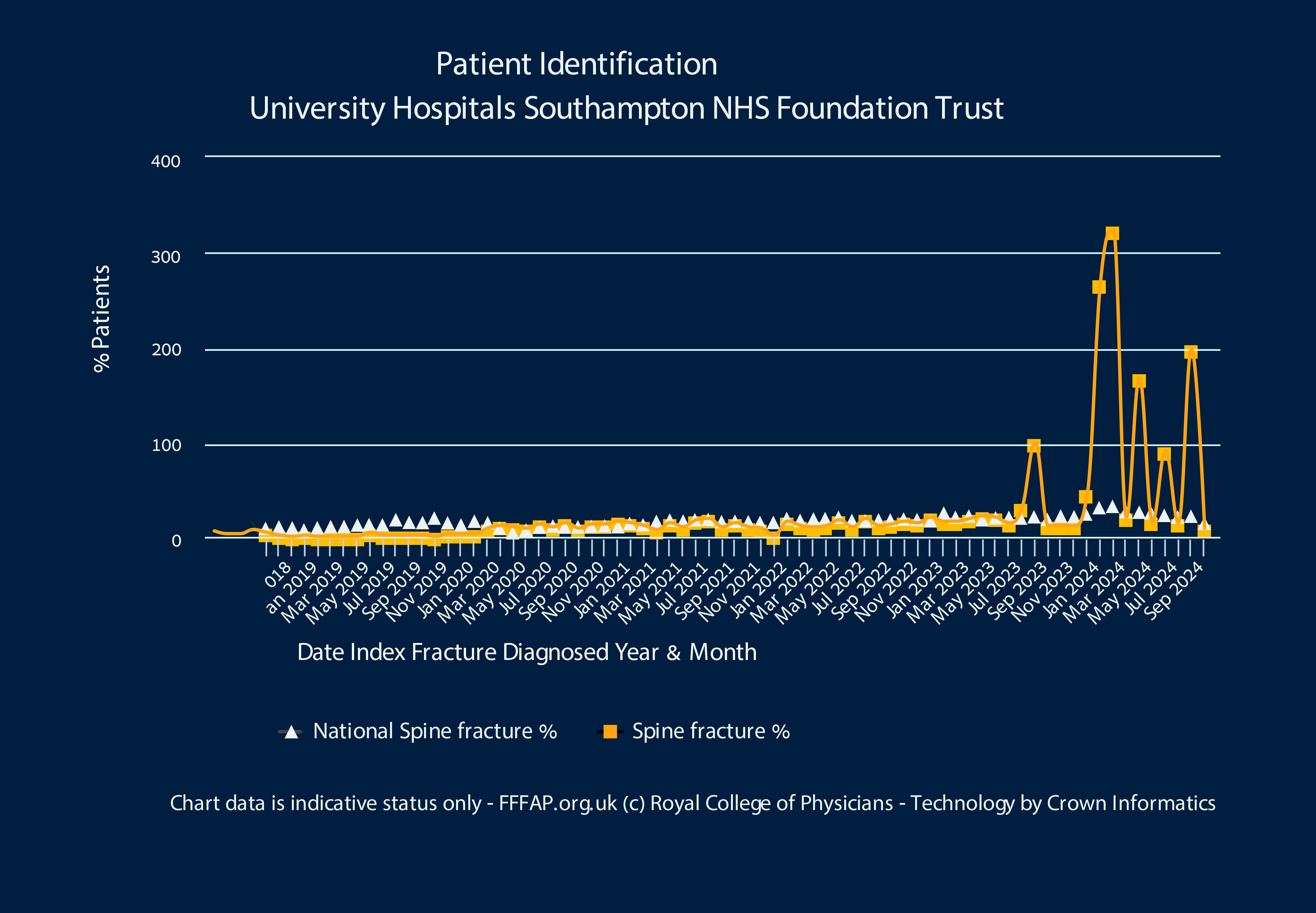
Early findings in the ADOPT study, show that Nanox.Al software improves the detection of spine fractures, an early sign of osteoporosis, outperforming UK National Health Service national average.

Discover the potential value of implementing AI in your healthcare system
Contact UsInnovative Healthcare Solutions for All
Cutting-Edge Medical AI Technology
Over a decade of Al imaging experience

Real Life Evidence

The great thing about Nanox as a vendor is that it’s agnostic in terms of PAC systems and able to integrate seamlessly

Al re-analysis of scans can catch missed fractures, as shown In the ADOPT Study across NHS locations. This innovation delivers proactive care for high fracture-risk patients who are otherwise missed

“I feel very lucky, I don’t think this would have been picked up without the AI technology.”

The ever-growing suite of opportunistic AI tools provided by Nanox.AI will allow for earlier detection of many important medical conditions such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and hepatic steatosis

Utilizing Nanox.AI to detect incidental CAC in patients can lead to early intervention with primary prevention strategies which would ultimately improve long term outcome and decrease healthcare costs

I had to come due to lung issues and along the way I was diagnosed with heart disease… maybe it was life saving
Partners & Collaborations




Discover the Power of AI in Early Detection of Chronic Conditions

Clinical Publications
Optimizing Preventive Cardiology: Harnessing AI For Early Detection Of Coronary Artery Disease,
Corewell Helth
Integrating into Electronic Medical Records (EMR) for Efficient Patient management
Leveraging AI for Opportunistic Screening: Identifying Coronary Artery Calcification on Non-ECG Gated Lung Cancer Screening Chest CT
Atlantic Health System
- 31.0% of patients undergoing lung cancer screening with low-dose chest CT were found to have moderate to severe CAC and did not have a known or existing diagnosis of CAD at the time of imaging
AI Empowering Early Detection Of CAD Patients For Improved Cardiac Care
Jefferson Einstein Hospital, Philadelphia
- Revenue Generation from AI Integration
- AI-Driven Procedures
- Future Revenue Potential
Opportunistic Screening of Coronary Artery Calcification on Non-gated Conventional CT Scans Using Artificial Intelligence; Rabin Medical Center
- AI-Based CAC Evaluation
- 694 patients were identified from incoming routine CT scans and were unknown to the system as CVD patients
 Nanox.AI
Nanox.AI


 Client portal
Client portal